The translation industry is undergoing a major shift. Businesses now face a choice that didn’t exist a decade ago: should they rely on AI translation systems that promise speed and cost savings, or stick with professional human translators who understand cultural nuance? Making the wrong choice can cost your business dearly in reputation, legal exposure, or missed market opportunities.
According to Gartner, 45% of organizations were piloting generative AI in 2023. Yet businesses still struggle with a fundamental question: when to use machine translation versus hiring professional linguists. The trade-offs between speed, accuracy, and cultural sensitivity create complex decisions that directly impact brand perception and regulatory compliance.
This article examines the critical factors that determine whether AI translation or human translation serves your specific needs. You’ll learn exactly which content types require human expertise, where automated systems excel, and how to build translation strategies that balance quality with efficiency.
TL;DR
|
Why it matters
Choosing between AI and human translation is not a binary decision; it’s a risk management choice that affects quality, compliance, timelines, and cost. A tiered strategy prevents expensive rework and protects brand trust while keeping velocity high.
AI translation vs human translation: how to choose
Quick answer
Rule of thumb: If errors could cause compliance issues, harm users, or damage brand trust, choose human (or hybrid with full review). |
The comparison of AI and human translators reveals distinct approaches to converting text between languages. Modern neural machine translation systems process content through algorithms trained on billions of multilingual text samples, identifying patterns and generating translations based on statistical probability. Human translators rely on years of linguistic training, cultural immersion, and contextual judgment to produce translations that preserve both meaning and intent.
AI translation efficiency vs human approaches becomes clear when examining speed metrics. AI systems can process thousands of words per minute, completing translations that would take human professionals days or weeks. A standard 10,000-word document requiring 48-72 hours for human translation can be machine-translated in minutes. This speed advantage has made AI translation the default choice for high-volume, time-sensitive content where perfection isn’t the primary concern.
However, the benefits of human translation over AI emerge clearly in accuracy measurements. Professional human translators consistently achieve 95-100% accuracy rates, while even advanced systems show limitations. A 2024 study published in PLOS ONE comparing DeepL, Google Translate, and CUBBITT found accuracy varied significantly by language pair and content complexity.
Research on legal document translation shows concerning gaps. A 2024 Heliyon study on legal texts highlights quality gaps and cautions against relying solely on MT for legal content.
The advantages and disadvantages of AI translation become more nuanced when considering context. AI systems struggle with ambiguity, cultural references, and texts where meaning depends heavily on unstated assumptions. A grammatically perfect AI translation might completely miss the original message’s intent. Human translators excel at reading between the lines, understanding implied meanings, and adapting content for cultural appropriateness in ways that purely algorithmic approaches cannot replicate.
Quality of translation extends beyond word-for-word accuracy. It encompasses tone preservation, cultural sensitivity, and the ability to handle specialized terminology correctly. In highly regulated fields like medicine or law, small translation errors can create life-threatening situations or legal liabilities. Language nuance recognition distinguishes professional human translation from machine output, particularly for marketing materials and communications where emotional resonance matters as much as literal accuracy.
The speed vs accuracy trade-off defines most translation decisions. Businesses must evaluate whether their content falls into categories where AI’s speed advantage outweighs potential accuracy issues, or whether the stakes require human expertise regardless of time constraints.
How Lara Translate bridges AI speed with professional quality
Lara Translate represents a specialized approach to translation AI that addresses many limitations found in general-purpose language models. Unlike broad AI systems trained on diverse internet content, Lara Translate was developed specifically for professional business translation, trained on curated parallel corpora of 25 million professionally reviewed translations. This focused training approach delivers higher contextual understanding in translation for business contexts while maintaining speed advantages.
The technology behind Lara Translate leverages Translation Language Models (T-LMs) rather than generic Large Language Models (LLMs). This distinction matters significantly for translation quality. General LLMs were trained primarily on English text, creating performance gaps when translating to and from non-English languages. Lara Translate specifically addresses this imbalance by optimizing for a growing number of the world’s most widely spoken languages — see the live list in the documentation — with equal attention to linguistic accuracy across all supported pairs, reaching over 2.8 billion native speakers.
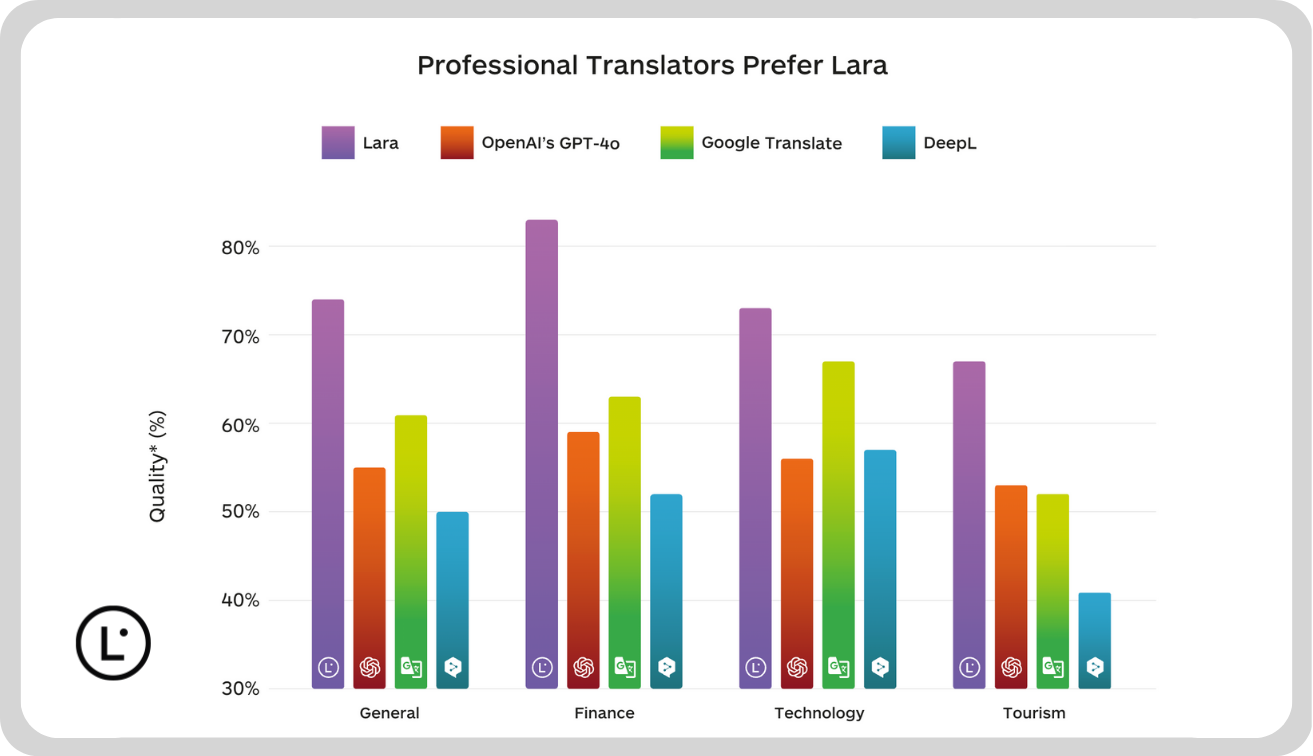
Performance benchmarks reveal substantial advantages. Lara Translate achieves translation speeds approximately 20 times faster than many competing solutions, with most translations completed in just over a second. This speed enables real-time translation applications previously impractical even with advanced AI systems. For businesses processing high volumes of multilingual content, these speed improvements directly translate to reduced operational costs and faster time-to-market.
The platform’s approach to domain specificity sets it apart from general translation services. Businesses can adapt Lara Translate with company-specific language assets, glossaries, and style guides, ensuring translations maintain brand voice and industry-specific terminology. This customization capability bridges a critical gap between AI’s processing speed and human translators’ understanding of organizational context.
Lara Translate’s integration capabilities extend its practical value through the Model Context Protocol (MCP). The new Lara Translate Agent automates localization tasks including project management and file preparation, reducing the manual coordination typically required for complex multilingual projects. Understanding how MCP enables seamless AI agent communication helps organizations leverage these advanced capabilities for more efficient workflows. For businesses managing translation workflows across multiple departments and content types, this orchestration capability significantly reduces administrative overhead.
Try AI + post-edit on one page
By enabling translation into English before processing by general LLMs (whose pricing structures favor English), Lara Translate reduces the per-word costs associated with multilingual AI workflows. This economic advantage becomes more pronounced at enterprise scale, where translation volumes can run into millions of words annually.
When is AI translation good enough?
Is AI translation reliable for your specific content? The answer depends entirely on what you’re translating and how the translated content will be used. AI translation excels with high-volume, time-sensitive material where perfect accuracy ranks lower than rapid deployment. Support teams using AI translation can respond to customer inquiries in dozens of languages instantly, providing faster service without hiring native speakers for every market.
Technical documentation represents an ideal use case for automated translation. Product specifications, user manuals, and knowledge base articles typically contain standardized terminology and straightforward, factual language. Research published in PLOS ONE examining medical abstracts translation found that advanced AI achieved 94% accuracy for technical “Results” sections, demonstrating AI’s strength with standardized content. The consistent vocabulary and minimal cultural context requirements mean machine translation can handle technical content with acceptable quality.
Internal communications within global organizations benefit significantly from AI translation. Email threads, project updates, and collaboration tools can incorporate real-time translation features that enable team members working in different languages to communicate seamlessly. The stakes for perfect cultural nuance remain lower for internal content than customer-facing materials, making AI translation’s speed-to-quality ratio appropriate for these scenarios.
E-commerce product descriptions, particularly for straightforward items, translate well through automated systems. Basic specifications, dimensions, materials, and usage instructions don’t require the cultural adaptation that marketing copy demands. For businesses managing thousands of SKUs across multiple markets, AI translation provides the scalability needed to maintain multilingual product catalogs without prohibitive translation costs. However, industries requiring deep cultural adaptation—such as gaming localization, where cultural nuances and player experience matter significantly—benefit from more sophisticated approaches that combine AI efficiency with human cultural expertise.
Content tiers provide a useful framework for AI translation decisions. Low-stakes content like user-generated comments, backend code documentation, or temporary internal memos can use raw AI translation to communicate basic meaning. Medium-stakes content like help articles or onboarding flows works well with AI translation plus light human review, especially when context accompanies the translations.
Real-time communication scenarios showcase AI translation’s unique advantages. Live chat support, video conferencing with multilingual participants, and immediate response systems require translation speeds no human translator can match. While the translations may lack polish, instant comprehension across language barriers enables business activities that wouldn’t otherwise be possible. The cost differences between AI and human translators become irrelevant when human translation timing makes entire business processes infeasible.
When is a human translator non-negotiable?
When to use human translation becomes non-negotiable for legal documents where precision directly affects contractual obligations and liability. Court proceedings, immigration documents, and government-issued certificates require certified sworn translations in many jurisdictions. These certified translations must come from translators who take legal oaths before court officers, guaranteeing that translations accurately match original documents. The 2024 Heliyon study on AI translation of legal texts found that 38% of machine-translated legal documents contained critical errors, with mistakes ranging from incorrect clause translations to omitted obligations that could invalidate contracts or create legal liability.
Medical and pharmaceutical content presents equally high stakes where is AI translation reliable becomes a life-or-death question. Prescription instructions, medical procedures, patient consent forms, and drug interaction warnings require absolute accuracy. Research examining Google Translate for emergency department discharge instructions found accuracy varied dramatically by language—92% for Spanish but only 81% for Chinese—with some inaccuracies having potential for clinically significant harm. Professional medical translators understand anatomical terminology, pharmaceutical nomenclature, and regulatory requirements governing medical documentation across different markets.
Marketing materials and brand communications demand human expertise for reasons extending beyond accuracy. Professional translators understand how humor translates across cultures, which metaphors resonate in different markets, and how brand voice should adapt while maintaining consistency. A slogan that works brilliantly in English might be meaningless, offensive, or laughable when literally translated to another language. The benefits of human translation over AI in marketing contexts include the ability to transcreate rather than merely translate—reimagining content to achieve equivalent impact in the target culture.

Financial documents including annual reports, investment prospectuses, and regulatory filings require human translation for both accuracy and compliance reasons. Financial regulators in many jurisdictions require certified translations for official documents. Beyond regulatory requirements, financial content often contains nuanced language around risk disclosures, forward-looking statements, and performance metrics where subtle mistranslations could mislead investors or violate securities laws.
Cultural adaptation projects like localizing entertainment content, adapting educational materials for different markets, or translating religious texts require deep cultural knowledge that AI systems cannot replicate. A 2020 Nature Communications paper reported news translation quality comparable to human professionals, but it fell short on fluency and cultural nuance. The case study AI vs human translation in literary translation provides clear examples—AI systems can process the words but miss the artistry, voice, and cultural references that give literature its meaning and impact.
High-value business communications including executive correspondence, investor presentations, partnership agreements, and crisis communications justify human translation costs through risk mitigation. These materials directly represent organizational leadership and shape critical business relationships. The reputational cost of translation errors in these contexts far exceeds the price of professional human translation.
Strategic framework: decision matrix
| Content type | Stakes | Method | Reviewer | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Internal updates, tickets, comments | Low | AI only | None | Time-sensitive; gist is enough |
| Knowledge base, manuals, UX strings | Medium | Hybrid (AI → post-edit) | Linguist | Enforce glossary & TM consistency |
| Product pages, onboarding flows, SEO articles | Medium-High | Hybrid → targeted human review | Editor + PM | Tone matters; sample back-translation |
| Legal, medical, financial, compliance docs | High | Human only | Certified/specialist | Certification/sworn translation may be required |
| Campaign slogans, brand voice, creative | High | Human (transcreation) | Creative lead | Cultural adaptation; market testing |
Successful translation strategies implement content-tiering systems that match translation methods to business value rather than applying uniform quality standards across all content. Translation programs shouldn’t pursue perfection for every piece of content. Instead, organizations should set quality targets based on business importance, allocating expensive resources proportionate to content impact.
High-stakes content demands human expertise and comprehensive review processes. This tier includes safety instructions, legal contracts, marketing campaigns, and landing pages where errors carry significant consequences. The costs justify investment because mistakes could damage brand reputation, create legal liability, or lose major market opportunities. Professional translation with native-speaker quality assurance represents the appropriate approach for this content category.
Medium-stakes content performs well with hybrid approaches combining AI translation and light human oversight. Help documentation, onboarding sequences, and user interface strings typically contain clear context that helps both automated systems and human reviewers produce quality output efficiently. The hybrid model delivers professional quality at substantially reduced cost compared to full human translation while maintaining acceptable quality standards.

Low-stakes content can rely on raw AI translation when communicating basic meaning suffices. User-generated comments, backend developer documentation, or temporary internal communications don’t justify expensive human translation. Automated translation enables comprehension across language barriers for content where polish matters less than accessibility.
Decision criteria for selecting approaches should evaluate content permanence, audience size, error consequences, and available timeline. Permanent public-facing content viewed by large audiences with severe error consequences requires human translation regardless of cost. Temporary internal content viewed by small technical audiences with minimal error impact can use raw AI translation to save resources.
Vendor selection for human translation services requires verifying credentials and expertise. Professional associations like CIOL or ITI maintain directories showing translators’ ISO 17100 compliance status. These certifications indicate adherence to quality standards, project management protocols, and professional ethics. For businesses lacking translation expertise, working with certified professionals reduces quality risks and provides recourse if translation disputes arise.
How do hybrid workflows actually work?
Hybrid translation workflows systematically combine AI speed with human contextual expertise to achieve productivity improvements over traditional approaches. These models typically structure work through three stages: automated draft generation via machine translation, guided post-editing by certified linguists, and final native-speaker quality assurance. This division of labor allows human translators to focus expertise where it adds most value rather than translating every word from scratch.
Automated draft generation handles the heavy lifting of word-by-word conversion, leveraging neural machine translation‘s speed and consistency. Modern translation management systems route content to appropriate engines based on language pair, content type, and previous performance metrics. Technical documentation might route through one engine while marketing copy uses another optimized for creative content.
Post-editing workflows provide translators with machine-generated drafts, reference materials, and collaboration tools within unified platforms. Professional linguists correct errors, refine style, and ensure cultural appropriateness while working significantly faster than translating from blank pages. The combined expense remains well below pure human translation while achieving comparable final quality.
Book a 15-min workflow audit
Translation memory systems amplify hybrid workflow efficiency by storing previously translated segments for reuse. When new content contains phrases or sentences already translated in past projects, the system automatically applies stored translations, ensuring consistency across related materials. This technology reduces both human and machine translation workload for repetitive content, particularly valuable for technical documentation, user interfaces, and recurring communications where terminology should remain consistent.
Quality assurance processes in hybrid workflows apply risk-appropriate review intensity. Critical content receives multi-level review including back-translation verification, where another translator independently translates content back to source language, revealing any meaning distortions. Lower-stakes content might receive only statistical quality checks or sampling-based review.
Continuous improvement through feedback loops enhances both machine and human performance over time. When human editors correct machine translation errors, those corrections can train custom AI models to reduce similar mistakes in future translations. Organizations with substantial ongoing translation needs realize compounding efficiency gains as their custom-trained systems improve.
The future: AI collaboration with human expertise
Translation AI will continue advancing, narrowing some accuracy gaps while still failing to replicate human cultural judgment. Future developments will likely improve AI’s handling of context, idiomatic expressions, and specialized terminology through larger training datasets and more sophisticated architectures. However, the fundamental limitation remains: AI systems lack lived experience in cultures they serve, missing subtle context that native speakers naturally understand.
The who wins in translation: human or AI question misframes the likely future. Rather than replacement, the industry will see continued evolution toward sophisticated hybrid models where AI handles mechanical aspects while humans provide judgment, cultural adaptation, and quality assurance. Professional translators will increasingly work as editors and cultural consultants rather than word-by-word converters, applying expertise where it adds most value.
Emerging agent-to-agent translation systems like those enabled by Model Context Protocol and Agent2Agent protocols represent the next frontier. These systems allow AI agents to coordinate translation workflows, manage terminology consistency, and handle project logistics that currently require human project managers. The automation of translation management tasks will reduce overhead costs while ensuring systematic quality processes.
Domain-specific translation AI models like Lara Translate will continue emerging to address limitations of general-purpose systems. These specialized models trained on professional translation corpora for specific industries or content types will deliver higher accuracy for their target domains while maintaining speed advantages. Organizations will increasingly select appropriate translation tools based on content type rather than applying single solutions universally.
Professional translator roles will evolve toward specialization in high-value content categories requiring deep expertise. Legal translators, medical translators, and literary translators will remain in strong demand for content where errors carry serious consequences or where artistry matters as much as accuracy. The middle market of straightforward business translation will see more AI automation with human oversight, while commodity translation of simple content will become almost entirely automated.
Conclusion: making informed translation decisions for your business
The choice between AI translation and human translation shouldn’t be binary. Smart translation strategies recognize that different content types require different approaches, with quality requirements, risk tolerance, and budget constraints varying across materials. Organizations that implement tiered translation systems matching methodology to content importance achieve better outcomes than those applying uniform approaches regardless of context.
AI translation efficiency vs human expertise creates complementary strengths rather than competing alternatives. AI excels at speed, consistency, and cost-effectiveness for high-volume content where perfect cultural nuance matters less than rapid comprehension. Human translators provide contextual understanding in translation, cultural adaptation, and specialized domain knowledge that remain beyond AI capabilities.
Critical content including legal documents, medical information, marketing materials, and executive communications justify human translation costs through risk mitigation and quality assurance. The potential consequences of translation errors in these categories far exceed the price difference between AI and professional translation.
Hybrid workflows combining AI draft generation with human post-editing deliver optimal cost-quality balance for medium-stakes content. This approach provides cost savings versus pure human translation while maintaining professional quality standards.
The translation cost-effectiveness equation must account for total cost of ownership beyond per-word translation fees. Factor error remediation costs, potential brand damage from poor translations, legal risks from mistranslated compliance documents, and lost opportunities from culturally inappropriate marketing. Organizations that optimize only for lowest translation cost often incur larger downstream expenses fixing problems that proper methodology selection would have prevented.
Technology platforms like Lara Translate provide enterprise-grade AI translation with optimizations for business contexts, supporting organizations implementing tiered translation strategies. Purpose-built translation AI trained on professional corpora delivers higher quality for business content than general-purpose language models while maintaining speed and cost advantages over pure human translation. Combined with human oversight for high-stakes content, specialized translation AI enables scalable multilingual operations that balance quality with efficiency.
FAQs
What’s the main difference between AI and human translation?
AI translation uses algorithms trained on large text datasets to generate translations based on statistical patterns and linguistic rules. Human translation relies on native language expertise, cultural knowledge, and contextual judgment. Research shows AI systems can achieve acceptable accuracy for straightforward content, while professional human translators consistently deliver higher accuracy. AI translates faster and costs less but cannot replicate human cultural understanding and contextual judgment.
Can AI translation handle technical documents accurately?
Yes, AI translation performs well with technical documentation, product specifications, and user manuals that contain standardized terminology and straightforward language. Research on technical medical content shows AI achieves up to 94% accuracy for standardized sections. Technical content’s consistent vocabulary and minimal cultural context requirements make it suitable for AI translation, particularly when human review verifies specialized terminology accuracy.
How much does human translation cost compared to AI?
Human translation typically costs significantly more per word than AI translation for common language pairs, while specialized language pairs cost even more. AI translation costs substantially less. Hybrid approaches combining AI with human post-editing fall somewhere in between. The cost difference varies significantly based on language pair complexity and content specialization, but hybrid workflows can provide substantial savings versus pure human translation.
Is there a middle ground between AI and human translation?
Yes, hybrid workflows provide the best balance for most business content. These approaches use AI to generate translation drafts quickly, then certified linguists review and refine the output for accuracy and cultural appropriateness. Hybrid methods deliver professional quality at lower cost than pure human translation while maintaining significantly higher accuracy than AI alone.
This article is about
- Key differences in AI translation vs human translation: accuracy, speed, cost, and cultural adaptation capabilities based on peer-reviewed research
- When AI translation works best: technical documentation, internal communications, and high-volume content
- When human translation is essential: legal documents, medical content, marketing materials, and certified translations
- Hybrid workflows combining AI speed with human expertise for optimal quality and cost efficiency
- Strategic frameworks for choosing between AI translation vs human translation based on content importance and risk
Have a valuable tool, resource, or insight that could enhance one of our articles? Submit your suggestion








